Rebecca’s hands trembled as she buttoned her jeans. Or tried to. For the third time that morning, the button refused to close. She sucked in her stomach, held her breath, and forced it shut. The metal bit into her skin, creating an angry red line across her midsection.
“When did this happen?” she whispered to her reflection.
But she knew. The stubborn belly fat that no amount of dieting seemed to fix. The afternoon energy crashes. The way she’d gained weight despite eating less. What Rebecca didn’t know was that her expanding waistline was screaming a warning about a serious metabolic condition ( insuline resistance ) that would soon change everything about her health—a condition affecting nearly 40 percent of young adults without them even knowing it.
Recent research reveals that metabolic dysfunction, specifically problems with how our bodies process insulin, often remains hidden for years, silently damaging your health while the only visible sign is that stubborn belly fat you can’t lose. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, about 97.6 million people in the United States ages 18 and older had prediabetes in 2021—a condition directly linked to this metabolic dysfunction.
The first visible warning sign? That belly fat you’ve been struggling with.
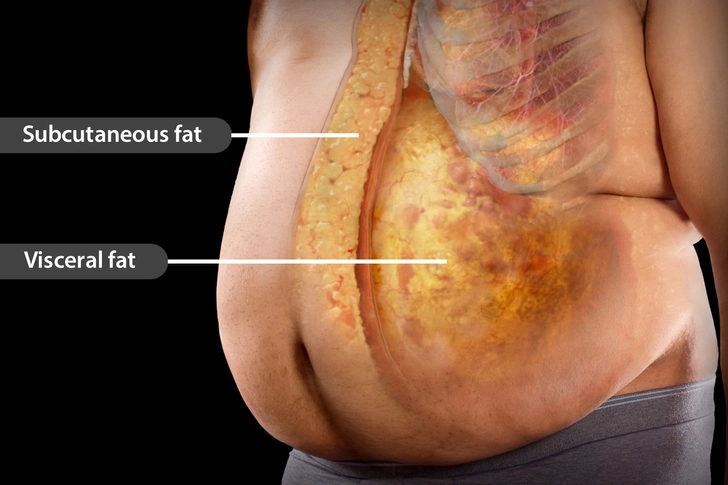
Understanding the Metabolic Storm Destroying Your Health
Here’s what nobody explains about metabolic dysfunction and fat storage: When your body develops problems processing insulin—from eating refined carbohydrates, constant snacking, or foods high in sugar—your cells become resistant to insulin’s signals. This creates a cascade of metabolic problems that go far beyond simple weight gain.
Picture your fat cells as storage units with locks. Usually, insulin acts like a security guard that opens those locks when you need to store or release energy. But when metabolic dysfunction develops, insulin stays elevated constantly. Those storage units can only receive deliveries—they can never ship anything out.
This is why you can eat fewer calories than ever and still gain weight. Your body literally cannot access its stored fat for energy. It’s like being broke with a million dollars locked in a vault you can’t open.
Recent studies from the StatPearls medical database reveal that the metabolic consequences of this dysfunction include hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperuricemia, elevated inflammatory markers, endothelial dysfunction, and a prothrombotic state. In simpler terms, this condition doesn’t just make you gain weight—it systematically damages your entire cardiovascular system.
The Hidden Epidemic Destroying Your Health, Insuline Resistance
Sarah, a 42-year-old marketing executive, discovered the brutal reality of this metabolic dysfunction the hard way. “I was doing everything ‘right,'” she told me. “Whole grain brown rice, sweet potato for dinner, high-fiber foods. I even started HIIT workouts three times a week.”
But her body fat percentage kept climbing despite her efforts to combat what she didn’t realize was a serious metabolic condition. Her energy crashed two hours after eating—a classic symptom. She couldn’t maintain her exercise routine because this dysfunction was exhausting her.
What Sarah didn’t realize was that she was trapped in a vicious cycle:
Morning: High-carb breakfast spikes insulin, worsening the condition Mid-morning: Blood sugar crashes, triggering intense cravings Lunch: More carbohydrates to “fuel” her day, another insulin spike Afternoon: Energy crash, desperate need for sugar or caffeine Evening: Too tired to cook, reaches for quick processed foods Night: Elevated insulin blocks fat burning all night long
Every meal was making her condition worse. Every “healthy” choice was deepening the metabolic trap.
The Shocking Statistics You Need to Know
The numbers are staggering. According to groundbreaking research from the University of Alabama at Birmingham, four in 10 adults, ages 18-44, have this metabolic dysfunction, and those affected have a significantly higher prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure, poor physical activity and high cholesterol.
Even more shocking? 50 percent of participants with this condition were not obese, meaning metabolic dysfunction can affect people of normal weight too.
Analysis from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) shows that this condition affects about 22% of United States adults older than 20 years, but a more recent analysis from 2021 found that 40% of US adults aged 18 to 44 are affected based on HOMA-IR measurements.
The truth about metabolic dysfunction is brutal: When you have this condition, your body treats a sweet potato almost the same as a candy bar. Both spike insulin. Both prevent fat burning. Both deepen the metabolic damage.
The Hidden Connection: Women’s Hormonal Health and Metabolic Dysfunction
For women, the story becomes even more complex. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), affecting 6-20% of women of reproductive age, is intrinsically linked to this metabolic dysfunction. According to research published in the Journal of Ovarian Research, insulin resistance affects some 65-70% of women with PCOS, with 70-80% of obese and 20-25% of lean women with PCOS exhibiting these characteristics.
The CDC explains that women with PCOS often have this metabolic dysfunction, which increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. The condition creates a vicious cycle: elevated insulin causes the ovaries to produce too much testosterone, which interferes with ovulation and worsens metabolic health.
Maria, 28, struggled with PCOS for years. “I couldn’t lose weight no matter what I tried. My periods were irregular, my skin was breaking out, and I felt exhausted all the time.” After addressing her underlying metabolic dysfunction through intermittent fasting and strategic nutrition, “Everything changed. I lost 35 pounds, my cycles normalized, and my energy came back. For the first time in years, I felt like myself again.”
Research from PMC shows that the hyperinsulinemia appears to be an important factor in maintaining hyperandrogenemia, acting directly to induce excess androgen production by theca cells and also as a co-gonadotropin, augmenting the effect of the increased LH stimulus seen in a majority of women with PCOS.
The Aging Factor: Why This Gets Worse Over Time
Here’s something that will shock you: aging itself is an inevitable risk factor for developing metabolic dysfunction. Advanced age is an important factor in increasing susceptibility to this condition. Research published in Frontiers in Endocrinology reveals that with increasing age, there is insufficient insulin secretion and a progressive decrease in glucose tolerance, as well as increasing resistance due to sarcopenia, excess adiposity and osteoporosis.

According to epidemiology, the prevalence of this condition and type 2 diabetes is high in the elderly population. This is associated with an increased prevalence of central obesity and increased visceral fat in the aging population.
A clinical study comparing elderly patients to younger subjects found that the senile group showed significant reduction in glucose tolerance, decreased insulin sensitivity, and marked reduction of first phase insulin response when compared with younger control groups.
Dr. Peterson’s research published in Science magazine mentions that older subjects clearly showed reduced insulin-stimulated muscle glucose metabolism compared to younger subjects. The investigators found increased fat accumulation in muscle and liver tissue and an approximately 40% reduction in mitochondrial oxidative and phosphorylation activity.
This means that even if you’re metabolically healthy now, aging itself will make you more susceptible to developing these problems—making early intervention absolutely critical.
Revolutionary Strategies to Reverse Metabolic Dysfunction
Here’s where everything changes. Where we stop playing defense and start winning the battle against metabolic dysfunction.
Intermittent Fasting: Your Metabolic Reset Button
Forget everything you’ve heard about eating six small meals a day. That advice keeps insulin elevated 24/7, making it impossible to burn fat and actually worsening metabolic dysfunction.
Recent studies published in NPJ Metabolic Health and Disease showed that 26-week intermittent fasting reduced homeostatic model assessment significantly without weight loss. A comprehensive meta-analysis published in eClinicalMedicine found that intermittent fasting may decrease waist circumference, fat mass, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, total cholesterol, fasting insulin, and systolic blood pressure.
The 16:8 Protocol:
- Fast for 16 hours (including sleep) to lower insulin
- Eat within an 8-hour window to give your metabolism time to recover
- No snacking between meals to prevent insulin spikes
A groundbreaking study published in Cell Metabolism found that five weeks of early time-restricted feeding improved insulin levels, insulin sensitivity, β cell responsiveness, blood pressure, and oxidative stress levels in men with prediabetes—even though food intake was matched to the control arm and no weight loss occurred.
Research from Clinical Diabetes & Endocrinology confirms that the majority of available research demonstrates that intermittent fasting is effective at reducing body weight, decreasing fasting glucose, decreasing fasting insulin, reducing this metabolic dysfunction, decreasing levels of leptin, and increasing levels of adiponectin.
What You Can Drink While Fasting (crucial for success):
- Water: Aim for half your body weight in ounces daily
- Black coffee: Unlimited, but stop by 2 PM to protect sleep
- Green tea: Excellent for fat burning, rich in antioxidants
- Herbal tea: Peppermint, chamomile, ginger – all allowed
- Apple cider vinegar: 1-2 tbsp in water, helps control blood glucose
- Bone broth: If struggling with hunger, 1 cup won’t break your fast
- Electrolytes: Add pink Himalayan salt to water if feeling weak
Strategic Nutrition for Metabolic Healing
You don’t need to go full ketogenic to reverse this condition, but you do need to dramatically reduce insulin-spiking foods. A network meta-analysis comparing different intermittent fasting regimens found that twice-per-week fasting (TWF) had the best combined effect in improving fasting glucose and metabolic dysfunction compared to other fasting regimens.
Foods That Worsen Metabolic Dysfunction:
- Grains: Bread, pasta, rice, quinoa, oats, cereals
- Sugary foods: Soft drinks, fruit juices, candy, cookies
- High-carb fruits: Bananas, grapes, mangoes, dried fruits
- Starchy vegetables: Potatoes, corn, peas
- Hidden sugars: Flavored yogurt, granola bars, sauces
- Processed foods: Chips, crackers, microwave meals
Foods That Support Metabolic Healing:
- Healthy fats: Avocado, olive oil, nuts, grass-fed butter
- Quality proteins: Wild salmon, grass-fed beef, eggs
- Non-starchy vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, cauliflower
- Low-carb fruits: Berries (limited), lemon, lime
- Healing foods: Apple cider vinegar, bone broth, fermented foods
Learn more about diabetes management from the CDC.
Advanced Timing Strategies for Maximum Results
When you eat matters almost as much as what you eat. Your body’s insulin sensitivity varies throughout the day, and optimizing meal timing can dramatically improve your metabolic health.
Optimal Meal Timing:
- 12 PM – Break fast: 3 eggs cooked in butter, half avocado, spinach
- 3 PM – Optional snack: Handful of nuts (only if needed)
- 6 PM – Final meal: Grilled salmon, roasted vegetables with olive oil
- After dinner: 30-minute walk at moderate pace
- 7 PM: Stop all eating, begin overnight fast
The Walking Protocol (critical for insulin sensitivity): Research shows that a 30-minute walk can reduce blood glucose spikes by up to 30%. This isn’t optional—it’s medicine for your metabolic health.
- Walk within 30 minutes of finishing dinner
- Maintain steady pace for 20-45 minutes
- No phones, no distractions—this is active meditation
- Track steps if helpful (aim for 3,000-4,000 post-meal)
Age-Specific Strategies for Different Life Stages
Young Adults (18-35): Prevention is Everything
Recent JMIR Public Health Research shows that the metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) was significantly associated with new-onset type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and older adults, emphasizing the importance of early intervention.
For young adults, the focus should be on prevention:
- Establish metabolic flexibility early through intermittent fasting
- Build muscle mass with resistance training to improve insulin sensitivity
- Avoid processed foods that trigger metabolic dysfunction
- Maintain healthy body composition regardless of weight

Middle Age (35-55): Damage Control and Reversal
This is the critical window where metabolic dysfunction often manifests visibly. According to Mayo Clinic research, risk of metabolic syndrome goes up with age, and up to one-third of U.S. adults have it.
Middle-aged strategies include:
- Aggressive intermittent fasting protocols (18:6 or OMAD 2-3x/week)
- Comprehensive hormone optimization especially for women approaching menopause
- Stress management as cortisol worsens metabolic dysfunction
- Sleep optimization as poor sleep increases this dysfunction by 40%
Older Adults (55+): Maintaining Independence
Research on aging and metabolic dysfunction shows that sarcopenic obesity (the coexistence of muscle loss and obesity) creates a particularly dangerous metabolic profile in older adults.
Strategies for older adults:
- Protein-focused nutrition to prevent muscle loss
- Gentle intermittent fasting (14:10 starting protocol)
- Resistance training to maintain muscle mass and insulin sensitivity
- Balance exercises to prevent falls related to metabolic complications
Real People, Real Transformations Across All Ages
Marcus, 52, Engineer: “My belly fat was so bad I couldn’t see my feet. Six months after starting intermittent fasting and reducing carbs, I’d lost 45 pounds. But the real victory? My pre-diabetes completely reversed.”
Marcus’s Daily Routine:
- 18:6 fasting window (eating 12 PM – 6 PM)
- Lunch: Large omelet with cheese and vegetables
- Dinner: Grass-fed steak with cauliflower and asparagus
- Evening: 45-minute walk while listening to podcasts
- Supplements: Berberine research shows effectiveness
Jennifer, 38, Teacher with PCOS: “PCOS made losing weight feel impossible. Once I understood the metabolic connection, everything changed. I’ve lost 32 pounds and my PCOS symptoms have virtually disappeared.”
Jennifer’s Meal Plan:
- 16:8 fasting (eating 11 AM – 7 PM)
- First meal: Greek yogurt with chia seeds and raspberries
- Lunch: Huge salad with grilled chicken and avocado
- Dinner: Baked salmon with herb butter and vegetables
- Post-dinner ritual: 30-minute neighborhood walk
David, 61, Retired: “I thought belly fat was just part of aging. My doctor wanted to put me on diabetes medication. Instead, I tried managing this naturally. One year later, no medication needed, and I feel 20 years younger.”
David’s Strategy:
- Progressed to OMAD (one meal a day) 3x per week
- OMAD days: Large meal at 2 PM with ribeye steak and huge salad
- Weight training 3x/week, daily evening walks
- Used continuous glucose monitor to track food impacts
Emma, 24, College Student: “I started gaining weight in college despite being active. Turned out I had early metabolic dysfunction. Intermittent fasting and cutting out processed foods completely transformed my energy and body composition.”
Emma’s College-Friendly Protocol:
- 16:8 fasting fitting around class schedule
- Campus dining: salads with protein, avoiding bread and desserts
- Study breaks: walks instead of snack breaks
- Weekend flexibility while maintaining core principles
Advanced Supplementation Protocols
While not required, certain supplements can dramatically accelerate recovery from metabolic dysfunction. Research shows these natural compounds can improve insulin sensitivity and support metabolic healing:
Tier 1: Essential Foundation
- Berberine (500mg 2x/day) – Research shows effectiveness similar to metformin
- Magnesium glycinate (400mg before bed) – Critical for insulin function
- Vitamin D3 (2000-5000 IU/day) – Low levels linked to metabolic dysfunction
- Omega-3 fatty acids (2-3g daily) – Reduces inflammation
Tier 2: Advanced Support
- Chromium (200-400mcg/day) – Improves glucose metabolism
- Alpha-lipoic acid (600mg/day) – Powerful insulin sensitizer
- Cinnamon extract (1000mg daily) – Enhances insulin sensitivity
- Apple cider vinegar (2 tbsp before meals) – Helps control blood glucose
Tier 3: Specialized Protocols
- Bitter melon extract (600mg daily) – Traditional metabolic remedy
- Gymnema sylvestre (400mg daily) – Blocks sugar absorption
- Probiotics (50+ billion CFU) – Gut health impacts metabolism
- NAD+ precursors – Support cellular energy production
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting supplements, especially if you take medications.
Breaking Through Common Roadblocks at Every Stage
“I’m always hungry when fasting!” Hunger comes in waves and typically disappears after 3-4 days. This is your body learning to access stored fat for energy. Drink water, black coffee, or tea. Add a pinch of salt if needed during the adaptation period.
“I have no energy without carbs!” This is temporary metabolic flexibility. Your body needs 2-3 weeks to become efficient at burning fat for fuel. Push through—the energy surge afterward is incredible. During transition, eat more healthy fats: add extra olive oil, eat more avocado, don’t fear grass-fed butter.
“Walking after dinner is hard to fit in!” This isn’t optional for metabolic health—it’s medicine. Studies show it can reduce blood glucose spikes significantly and improve insulin sensitivity. Make it non-negotiable by:
- Scheduling it like any important appointment
- Finding a walking buddy for accountability
- Using the time for phone calls or podcasts
- Starting with just 10 minutes if needed
“My family won’t support this eating style!” You don’t need to announce your metabolic healing plan. Simply say you’re not hungry at breakfast or you’re eating within a window for health reasons. Lead by example—your results will speak louder than words.
“I’m traveling constantly for work!” Travel doesn’t have to derail progress:
- Pack nuts, jerky, and other metabolically-friendly snacks
- Research restaurant options that support metabolic healing
- Maintain walking routine even if meal timing shifts
- Use hotel gyms or bodyweight exercises in your room
- Don’t let perfect be the enemy of good
“I’ve tried everything and nothing works!” You haven’t tried fixing the root cause. Most approaches treat symptoms while ignoring the underlying metabolic dysfunction. This protocol addresses the fundamental problem that makes everything else fail.
For more information about diabetes and metabolic health, visit the American Diabetes Association.
Your Comprehensive 30-Day Metabolic Reset Plan
Week 1: Foundation Building
Goal: Establish metabolic flexibility basics
Daily Protocol:
- Start 14:10 fasting (work up to 16:8)
- Eliminate obvious sugars and refined carbohydrates
- Walk 20 minutes after largest meal
- Track energy levels 2-3 hours after eating
Week 1 Sample Day:
- 10 AM: Break fast with scrambled eggs in butter, sautéed spinach
- 2 PM: Grilled chicken thighs, large mixed salad with olive oil
- 6 PM: Baked cod, steamed broccoli, side of sauerkraut
- 6:30 PM: 20-minute walk around neighborhood
- Track: Hunger levels, energy, sleep quality
Week 2: Acceleration Phase
Goal: Achieve consistent 16:8 fasting with carb reduction
Daily Protocol:
- Achieve 16:8 fasting daily
- Reduce total carbs below 100g/day
- Add apple cider vinegar before meals (2 tsp in water)
- Prioritize 7-8 hours of sleep nightly
Week 2 Sample Day:
- 12 PM: Tuna salad (made with avocado) on lettuce wraps
- 4 PM: Handful of macadamia nuts (only if needed)
- 7 PM: Beef stir-fry with low-carb vegetables in coconut oil
- 7:30 PM: 30-minute walk at brisk pace
- Track: Waist measurements, mood, cravings intensity
Week 3: Optimization Phase
Goal: Intensive metabolic reset with advanced protocols
Daily Protocol:
- Try one 24-hour fast (with medical clearance)
- Reduce carbs below 50g/day for deeper ketosis
- Begin resistance training 2x/week
- Add magnesium supplementation (400mg before bed)
Week 3 Sample Day:
- 1 PM: Large omelet with cheese, mushrooms, bell peppers
- 6 PM: Grilled salmon, cauliflower rice, asparagus with hollandaise
- Post-dinner: 35-minute walk plus 10 minutes stretching
- Track: Ketone levels (if using strips), strength gains, body composition
Week 4: Mastery and Integration
Goal: Establish sustainable long-term protocols
Daily Protocol:
- Consistent 16:8 or 18:6 fasting based on preference
- Dial in your personal carb tolerance
- Establish sustainable exercise routine
- Plan your next 30 days of continued optimization
Week 4 Sample Day:
- 12 PM: Leftover protein from dinner, half avocado, cucumber slices
- 5:30 PM: Grass-fed burger (no bun), small sweet potato, big salad
- Evening routine: 40-minute walk, meal prep for tomorrow
- Track: Progress photos, measurements, energy levels 1-10 scale
Advanced Strategies for Stubborn Cases
The 72-Hour Reset Protocol
For severe metabolic dysfunction requiring rapid intervention (medical supervision required):
Extended Fasting Protocol:
- 48-72 hour fast once monthly (medical supervision essential)
- Electrolyte supplementation throughout
- Gradual re-feeding with fat and protein
- Monitor blood glucose and ketones
Who Should Consider This:
- Severe metabolic dysfunction (HOMA-IR >4.0)
- Failed response to standard protocols after 3 months
- Medical supervision available
- No contraindications (pregnancy, eating disorders, diabetes medications)
Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Optimization
Modern technology allows real-time feedback on your metabolic state:
Benefits of CGM:
- See immediate food impacts on blood sugar
- Identify hidden trigger foods
- Optimize meal timing and composition
- Track progress objectively
Key Metrics to Watch:
- Fasting glucose (goal: 80-90 mg/dL)
- Post-meal peaks (goal: <140 mg/dL)
- Time in range (goal: >70% between 70-140 mg/dL)
- Dawn phenomenon patterns
Precision Medicine Approaches
Genetic testing can reveal personalized strategies:
Relevant Genetic Markers:
- APOE genotype: Affects fat metabolism and cardiovascular risk
- FTO gene: Influences satiety and food choices
- TCF7L2: Impacts diabetes risk and insulin sensitivity
- ADIPOQ: Affects adiponectin levels and metabolic health
The Science of Metabolic Flexibility
Understanding how your metabolism works helps optimize your approach. Metabolic flexibility is your body’s ability to switch between burning carbohydrates and fats for fuel based on availability and demand.
The Four Metabolic States
- Fed State (0-4 hours after eating)
- High insulin, glucose burning primary
- Fat storage active, fat burning minimal
- Blood sugar elevated then declining
- Post-Absorptive State (4-12 hours)
- Insulin declining, transitioning to fat burning
- Liver glycogen being depleted
- Ketone production beginning
- Fasted State (12-24 hours)
- Low insulin, fat burning primary
- Ketone production increasing
- Growth hormone elevation
- Extended Fast (24+ hours)
- Autophagy activation
- Maximum fat burning and ketosis
- Cellular repair processes active

Optimizing Each State
Fed State Optimization:
- Choose foods that minimize insulin spikes
- Include protein and fat with any carbohydrates
- Stop eating 3-4 hours before bed
Transition Optimization:
- Light physical activity to deplete glycogen
- Avoid snacking to allow insulin to fall
- Stay hydrated as metabolism shifts
Fasted State Optimization:
- Maintain electrolyte balance
- Light exercise enhances fat burning
- Monitor for any adverse symptoms
Extended Fast Optimization:
- Medical supervision recommended
- Enhanced autophagy and cellular repair
- Gradual re-feeding essential
Addressing Common Health Conditions
Metabolic Dysfunction and Thyroid Health
Thyroid dysfunction and metabolic problems often coexist. Hypothyroidism can lead to insulin resistance, while metabolic dysfunction can impair thyroid hormone conversion.
Integrated Approach:
- Address both conditions simultaneously
- Monitor thyroid function during metabolic improvements
- Ensure adequate iodine, selenium, and zinc
- Consider timing of thyroid medications with fasting
Metabolic Dysfunction and Mental Health
Research shows strong connections between metabolic health and brain function. Poor metabolic health can contribute to depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
Brain-Metabolic Connection:
- Ketones provide superior brain fuel
- Stable blood sugar improves mood
- Reduced inflammation benefits mental health
- Better sleep from metabolic optimization
Metabolic Dysfunction and Autoimmune Conditions
Many autoimmune conditions involve inflammatory processes that worsen with metabolic dysfunction.
Anti-Inflammatory Approach:
- Eliminate inflammatory foods
- Support gut health with fermented foods
- Optimize vitamin D status
- Manage stress through metabolic stability
The Future of Metabolic Health
Emerging research reveals exciting developments in understanding and treating metabolic dysfunction:
Circadian Biology
New research emphasizes the importance of eating in alignment with circadian rhythms. Early time-restricted eating (eTRF) shows superior results compared to late eating windows.
Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in metabolic health. Certain bacterial strains can improve insulin sensitivity, while others worsen it.
Personalized Nutrition
Genetic testing and continuous monitoring allow for increasingly personalized approaches to metabolic optimization.
Novel Therapeutics
New medications and supplements targeting specific metabolic pathways show promise for those with severe dysfunction.
Creating Your Support System
Medical Team Assembly
Build a healthcare team that understands metabolic approaches:
Essential Team Members:
- Functional medicine physician who understands root causes
- Endocrinologist familiar with natural approaches
- Registered dietitian experienced in low-carb/intermittent fasting
- Personal trainer knowledgeable about metabolic exercise
Family and Social Support
Strategies for Family Buy-In:
- Lead by example rather than preaching
- Share your results and energy improvements
- Cook family-friendly versions of metabolic meals
- Explain health benefits without overwhelming with details
- Find compromise solutions for family meals
- Create new traditions around health-promoting activities
Building Your Community:
- Join online communities focused on metabolic health
- Find local walking or hiking groups
- Connect with others doing intermittent fasting
- Share recipes and meal prep strategies
- Celebrate non-scale victories together
Long-Term Maintenance Strategies
The 80/20 Approach for Sustainability
Once you’ve reversed metabolic dysfunction, maintaining results requires a sustainable approach:
Daily Consistency (80%):
- Maintain regular eating windows most days
- Prioritize whole foods and minimize processed options
- Continue post-meal walking habit
- Preserve sleep and stress management routines
Flexibility for Life (20%):
- Allow for social occasions and travel
- Don’t stress about perfect adherence
- Get back on track quickly after deviations
- Focus on long-term trends over daily perfection
Monitoring and Adjustments
Quarterly Health Checks:
- Waist circumference measurements
- Fasting insulin and glucose levels
- HOMA-IR calculation
- Body composition analysis
- Energy and mood assessments
Annual Comprehensive Assessment:
- Complete metabolic panel
- Inflammatory markers (CRP, ESR)
- Thyroid function
- Vitamin D and B12 levels
- Cardiovascular risk markers
Warning Signs to Watch For
Early indicators that metabolic dysfunction might be returning:
- Increased waist circumference (>2 inches)
- Return of post-meal energy crashes
- Intensifying sugar cravings
- Declining sleep quality
- Increased inflammatory symptoms
Immediate Action Steps:
- Return to stricter eating windows
- Eliminate processed foods completely
- Increase physical activity
- Assess and address stressors
- Consider medical evaluation if symptoms persist
Special Populations and Considerations
Athletes and High Performers
Athletic individuals require modified approaches to maintain performance while optimizing metabolic health:
Athlete-Specific Protocols:
- Strategic carb timing around training
- Longer eating windows on heavy training days
- Focus on nutrient timing rather than restriction
- Monitor performance metrics alongside metabolic markers
Shift Workers and Irregular Schedules
People with irregular schedules face unique challenges but can still achieve metabolic success:
Shift Work Strategies:
- Align eating windows with circadian rhythms when possible
- Use light therapy to support circadian health
- Prioritize consistency within irregular patterns
- Focus on food quality when timing is challenging
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnancy requires special considerations for metabolic health:
Safe Approaches During Pregnancy:
- Focus on nutrient density over restriction
- Avoid extended fasting periods
- Maintain stable blood sugar through protein and healthy fats
- Work closely with healthcare providers
- Prioritize sleep and stress management
Children and Adolescents
Young people need age-appropriate approaches to metabolic health:
Youth-Friendly Strategies:
- Focus on whole foods rather than restriction
- Encourage natural eating patterns
- Promote physical activity and sleep
- Address underlying causes of metabolic dysfunction
- Involve pediatric endocrinologists when necessary
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Toxin Reduction for Metabolic Health
Environmental toxins can disrupt metabolic function through endocrine disruption:
Key Toxin Sources to Address:
- Plastics: Use glass and stainless steel containers
- Personal care products: Choose organic, toxin-free options
- Household cleaners: Switch to natural alternatives
- Water quality: Install appropriate filtration systems
- Air quality: Use air purifiers and houseplants
Sleep Optimization for Metabolic Function
Quality sleep is non-negotiable for metabolic health. Poor sleep can increase insulin resistance by up to 40% in just one week.
Sleep Hygiene Protocol:
- Consistent sleep and wake times
- Cool, dark bedroom environment
- Blue light blocking 2 hours before bed
- Magnesium supplementation if needed
- Address sleep disorders like sleep apnea
Sleep and Metabolism Connection:
- Growth hormone release during deep sleep
- Cortisol regulation affects insulin sensitivity
- Appetite hormones (leptin/ghrelin) depend on adequate sleep
- Circadian rhythm disruption worsens metabolic dysfunction
Stress Management for Metabolic Recovery
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which directly worsens insulin resistance and promotes abdominal fat storage.
Evidence-Based Stress Reduction:
- Meditation: 10-20 minutes daily reduces cortisol
- Deep breathing: 4-7-8 technique activates parasympathetic nervous system
- Nature exposure: Forest bathing reduces stress hormones
- Social connection: Strong relationships buffer stress response
- Purposeful activity: Engaging in meaningful work reduces chronic stress
Movement Beyond Exercise
Incorporating movement throughout the day supports metabolic health beyond formal exercise sessions:
Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT):
- Take stairs instead of elevators
- Stand or walk during phone calls
- Park farther away from destinations
- Use a standing desk for part of the workday
- Take movement breaks every hour
The Power of Walking: Walking is perhaps the most underrated metabolic intervention. Recent research shows that:
- 10,000 steps daily significantly improves insulin sensitivity
- Post-meal walks reduce glucose spikes by 20-30%
- Walking meetings improve both metabolism and creativity
- Nature walks provide additional stress-reduction benefits
Troubleshooting Common Plateaus
Weight Loss Plateaus
When weight loss stalls despite following protocols:
Plateau-Breaking Strategies:
- Vary fasting windows: Alternate between 16:8, 18:6, and occasional OMAD
- Carb cycling: Introduce strategic higher-carb days
- Increase protein intake: Boost metabolic rate through thermic effect
- Change exercise routine: Add new stimulus to prevent adaptation
- Address stress and sleep: Hidden factors affecting progress
Metabolic Adaptation
Long-term caloric restriction can slow metabolism. Combat this with:
Metabolic Restoration Techniques:
- Refeed days: Strategic higher-calorie days
- Exercise variation: Prevent adaptation with new challenges
- Hormone optimization: Address thyroid, testosterone, or other hormonal issues
- Patience: Allow body time to reset metabolic rate
Emotional and Psychological Barriers
Metabolic dysfunction often has psychological components:
Addressing Emotional Eating:
- Identify trigger emotions and situations
- Develop non-food coping strategies
- Practice mindful eating techniques
- Consider professional counseling if needed
- Build self-compassion for the healing journey
The Economics of Metabolic Health
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Investing in metabolic health provides significant long-term economic benefits:
Immediate Costs:
- Quality food (offset by eating less frequently)
- Supplements (optional but beneficial)
- Gym membership or equipment
- Medical testing and consultations
Long-Term Savings:
- Reduced diabetes medication needs
- Lower cardiovascular disease risk
- Decreased healthcare utilization
- Improved work productivity
- Enhanced quality of life

Budget-Friendly Strategies
Metabolic health doesn’t require expensive interventions:
Low-Cost High-Impact Interventions:
- Intermittent fasting: Costs nothing, saves money on food
- Walking: Free exercise with maximum metabolic benefit
- Home cooking: Less expensive than processed foods
- Basic supplements: Magnesium and vitamin D are inexpensive
- Sleep optimization: Costs little but provides huge returns
Global Perspectives on Metabolic Health
Traditional Wisdom Meets Modern Science
Many traditional cultures naturally incorporated metabolic health principles:
Lessons from Blue Zones:
- Natural fasting periods: Traditional societies often had limited food availability
- Whole food diets: Processed foods are recent inventions
- Active lifestyles: Daily movement was necessity, not choice
- Social connections: Strong communities support overall health
- Purpose and meaning: Psychological wellbeing affects metabolic health
Cultural Adaptations
Metabolic health principles can be adapted to any cultural food tradition:
Mediterranean Approach:
- Olive oil as primary fat source
- Fish and seafood emphasis
- Limited refined grains
- Natural fasting traditions during religious observances
Asian Approaches:
- Green tea consumption
- Fermented foods for gut health
- Smaller portion sizes
- Walking as primary transportation
Traditional American:
- Farm-to-table whole foods
- Seasonal eating patterns
- Physical labor as exercise
- Family meals without distractions
Research and Future Directions
Emerging Biomarkers
New laboratory tests provide better insights into metabolic health:
Advanced Testing Options:
- Continuous glucose monitoring: Real-time glucose patterns
- Advanced lipid panels: Particle size and density analysis
- Inflammatory markers: IL-6, TNF-alpha, high-sensitivity CRP
- Hormone panels: Comprehensive assessment of metabolic hormones
- Micronutrient testing: Identify specific deficiencies
Cutting-Edge Interventions
Promising new approaches being researched:
Innovative Therapies:
- Cold thermogenesis: Controlled cold exposure to improve metabolism
- Heat therapy: Sauna use for metabolic benefits
- Light therapy: Circadian rhythm optimization
- Breathwork: Specific breathing patterns for metabolic health
- Probiotics: Targeted bacterial strains for metabolic improvement
Personalized Medicine
The future of metabolic health is increasingly personalized:
Precision Approaches:
- Genetic-based nutrition recommendations
- Microbiome-guided dietary interventions
- AI-powered lifestyle optimization
- Wearable technology integration
- Predictive modeling for disease prevention
Taking Action: Your Next Steps
Immediate Actions (This Week)
- Clear out processed foods from your kitchen
- Start a 14:10 eating window to begin metabolic adaptation
- Take baseline measurements (weight, waist circumference, photos)
- Schedule a comprehensive metabolic panel with your doctor
- Begin post-meal walking after your largest meal of the day
Short-Term Goals (This Month)
- Achieve consistent 16:8 intermittent fasting
- Eliminate refined sugars and grains from your diet
- Establish a sustainable exercise routine including both cardio and resistance training
- Optimize sleep hygiene for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly
- Build your support system of family, friends, and healthcare providers
Medium-Term Objectives (3 Months)
- See measurable improvements in waist circumference and energy levels
- Achieve metabolic flexibility with stable energy throughout the day
- Normalize blood markers including fasting insulin and glucose
- Establish sustainable lifestyle patterns that support long-term success
- Address any underlying health conditions that may be complicating your progress
Long-Term Vision (1 Year and Beyond)
- Complete reversal of metabolic dysfunction with normal blood markers
- Sustainable lifestyle that maintains metabolic health without extreme measures
- Improved overall health with reduced risk of chronic diseases
- Enhanced quality of life with stable energy, better mood, and optimal body composition
- Become a positive example for family and friends seeking similar transformation
Final Thoughts: Your Metabolic Transformation Starts Now
The science is clear, the methods are proven, and thousands of people have successfully reversed their metabolic dysfunction using these exact strategies. The only question remaining is whether you’ll join them.
Rebecca, whose story opened this article, sent me this message eight months after beginning her metabolic transformation: “I’m wearing jeans two sizes smaller than when I started. But that’s not the real victory. The victory is that my latest blood work shows no signs of pre-diabetes. My insulin levels are normal. My energy is stable all day. I feel like I’ve reclaimed my life.”
David, the 61-year-old retiree, wrote: “My doctor said my metabolic markers look better than most 40-year-olds. I feel stronger, more energetic, and more optimistic about my future than I have in decades.”
Jennifer, struggling with PCOS, shared: “My cycles are regular for the first time in years. My skin is clear. My energy is through the roof. Most importantly, I understand my body now. I know how to maintain this for life.”
These aren’t exceptional cases—they’re the natural result of addressing the root cause of metabolic dysfunction rather than just treating symptoms.
Your belly fat isn’t just about appearance. It’s a warning signal that your metabolic health is in danger. Every day you wait, the dysfunction deepens. Every high-carb meal adds to the damage. Every year of aging makes reversal more challenging.
But here’s the profound hope: Your body wants to heal. Given the right conditions—stable insulin levels, adequate nutrients, proper rest, and regular movement—it knows exactly how to restore healthy metabolic function.
The path is clear. The tools are available. The support is here. The only thing missing is your decision to start.
Your metabolic transformation doesn’t begin tomorrow, or next Monday, or next month. It begins right now, with your very next meal choice, your next decision to take a walk, your next commitment to prioritize your health.
The clock is ticking on your metabolic health. But unlike many things in life, this is entirely within your control. You have the power to reverse years of metabolic damage and reclaim your health.
What’s it going to be?
This article is for educational purposes only and focuses on natural approaches to managing metabolic health. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have existing health conditions, take medications, or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Comprehensive FAQ: Everything You Need to Know
How Do I Know If I Have Metabolic Dysfunction?
The most visible sign is excess belly fat that won’t budge despite diet and exercise. Other symptoms include:
- Energy crashes 2-3 hours after meals (classic sign)
- Intense sugar cravings throughout the day
- Difficulty losing weight despite calorie restriction
- Brain fog and difficulty concentrating
- Frequent hunger even after eating
- Dark patches of skin around neck, armpits (acanthosis nigricans)
- High blood pressure and elevated triglycerides
- Irregular periods in women or erectile dysfunction in men
Blood tests revealing fasting insulin above 5 μIU/mL or HOMA-IR above 2.5 confirm the diagnosis.
Can This Metabolic Dysfunction Be Completely Reversed?
Yes, absolutely! Unlike type 2 diabetes, early-stage metabolic dysfunction is completely reversible when caught early. Your cells can regain their sensitivity through:
- Consistent intermittent fasting to give insulin levels time to normalize
- Strategic carbohydrate reduction to stop triggering constant insulin spikes
- Regular post-meal walks to improve insulin sensitivity immediately
- Quality sleep to support metabolic recovery
- Stress management to prevent cortisol from worsening the condition
- Resistance training to build insulin-sensitive muscle tissue
Most people see significant improvements within 4-6 weeks of following the complete protocol.
What’s the Difference Between This Condition and Diabetes?
Think of metabolic dysfunction as the fire alarm before the house burns down:
Early Metabolic Dysfunction:
- Insulin levels are high, but blood sugar appears normal
- Your pancreas is working overtime to overcome cellular resistance
- Belly fat accumulates as the primary visible warning sign
- Completely reversible with lifestyle changes
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Your pancreas can no longer keep up with severe metabolic dysfunction
- Blood sugar rises because insulin resistance has become overwhelming
- Multiple medications often needed due to advanced cellular damage
- Much harder to reverse, but still possible by addressing underlying metabolic issues
The goal is to catch and reverse dysfunction before it progresses to diabetes.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
Metabolic recovery happens in predictable stages:
Week 1-2: Initial improvements
- Reduced sugar cravings as insulin begins responding better
- Slightly improved sleep quality
- Beginning of energy stabilization
Week 3-4: Accelerated healing
- Noticeable reduction in belly fat and waist circumference
- Stable energy throughout the day (major milestone)
- Significant reduction in hunger between meals
Month 2-3: Major transformation
- Blood markers dramatically improved
- Exercise becomes easier and more enjoyable
- Mental clarity and mood improvements
Month 4-6: Complete transformation
- Normal insulin levels on blood tests
- Sustained energy without blood sugar swings
- Sustainable lifestyle that maintains results long-term
Can I Exercise My Way Out of This Condition?
Exercise helps significantly, but it cannot overcome a poor diet that continuously spikes insulin. Here’s the reality:
What Works for Metabolic Health:
- Post-meal walks (improves insulin sensitivity by 20-30% immediately)
- Resistance training (builds insulin-sensitive muscle tissue)
- Short HIIT sessions (enhances insulin sensitivity once base health improves)
What Doesn’t Work:
- Excessive cardio (can worsen the condition by raising cortisol levels)
- Exercise without dietary changes (cannot overcome constant insulin spikes from poor food choices)
- Working out while eating high-carb foods (fighting the condition with one hand while feeding it with the other)
Remember: You cannot out-exercise metabolic dysfunction if you’re constantly spiking insulin with food choices.
What About Medications for This Condition?

While medications like metformin can help manage symptoms, they don’t address the root cause. Many people successfully reverse metabolic dysfunction naturally through:
Natural Approaches That Work:
- Intermittent fasting (often more effective than medications)
- Low-carb nutrition (directly targets the cause)
- Regular movement (builds long-term resilience)
- Stress management (prevents cortisol from worsening the condition)
When to Consider Medication:
- If lifestyle changes aren’t improving the condition after 3-4 months
- If dysfunction is severe and needs immediate intervention
- If you have additional health conditions complicating recovery
- As a bridge while implementing lifestyle changes
Always work with a healthcare provider who understands both natural approaches and medication options.
Is This Safe for Everyone?
The basic principles are safe for most people, but certain populations need modified approaches:
Special Considerations:
- Pregnant/breastfeeding women: Focus on nutrient density, avoid extended fasting
- People with eating disorders: Work with specialized healthcare providers
- Those on diabetes medications: Require medical supervision to adjust medications
- Children and adolescents: Need age-appropriate modifications
- People with serious medical conditions: Should work closely with healthcare providers
Generally Safe for:
- Healthy adults without contraindications
- People with early-stage metabolic dysfunction
- Those wanting to prevent future metabolic problems
- Individuals looking to optimize existing health
What If I Have PCOS or Other Hormonal Issues?
PCOS and metabolic dysfunction are intimately connected. Research shows that 65-70% of women with PCOS have insulin resistance, making metabolic approaches extremely effective for PCOS management.
PCOS-Specific Benefits:
- Improved insulin sensitivity often normalizes hormone levels
- Weight loss becomes possible when insulin resistance is addressed
- Menstrual cycles often regulate naturally
- Fertility improvements frequently occur
- Skin and hair symptoms often improve
Modified Approach for PCOS:
- Slightly longer eating windows initially (14:10 or 16:8)
- Focus on anti-inflammatory foods
- Include specific supplements like inositol and spearmint tea
- Work with healthcare providers familiar with PCOS and metabolic approaches
How Do I Handle Social Situations and Holidays?
Social eating doesn’t have to derail your progress:
Social Situation Strategies:
- Eat before going to events to avoid temptation
- Bring a metabolically-friendly dish to share
- Focus on socializing rather than food
- Choose protein and vegetables when possible
- Don’t stress about occasional deviations
Holiday Approaches:
- Maintain your eating window even if food choices vary
- Plan for special occasions by being stricter other days
- Focus on traditions beyond food
- Get back on track immediately after events
- Remember that consistency matters more than perfection
Travel Tips:
- Pack approved snacks for flights and road trips
- Research restaurant options in advance
- Maintain walking routine regardless of location
- Use hotel gyms or bodyweight exercises in your room
- Stay hydrated and prioritize sleep despite schedule changes
What About Family Members Who Don’t Support This?
Family dynamics can be challenging, but you can succeed even without full family support:
Strategies for Unsupportive Family:
- Lead by example rather than preaching
- Focus on your own meals without commenting on theirs
- Share your results and energy improvements
- Find compromises for family meals
- Explain health benefits without overwhelming them with details
Building Family Buy-In:
- Cook family-friendly versions of your meals
- Include them in physical activities like walks
- Share success stories and research when they show interest
- Be patient—your results will speak louder than words
- Focus on what you can control rather than trying to change others
Creating New Traditions:
- Replace food-centered activities with movement-based ones
- Start family walking or hiking traditions
- Involve kids in cooking healthy meals
- Make health and energy the family focus rather than just appearance
Remember: Your transformation can inspire others, but you can’t force anyone else to change. Focus on your own health journey and let your results be the example that motivates others.
For more information, please take a look at the blogs below:
- Dr. Jason Fung’s Research on Insulin Resistance
- Intermittent Fasting Research in New England Journal of Medicine
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis Guidelines
- Berberine Studies from PubMed
- CDC Information on Diabetes and Heart Disease
- PCOS and Insulin Resistance Research
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
We have compiled some of our top articles for your reading pleasure. Take a look at them whenever you have the time.
- Hearing Loss and Cognitive Decline In Older Adults
- The Ultimate Guide to Boosting Your Oral Health
- The Power of Water: Harnessing its Benefits for Optimal Human Health
- Dental Dietary Supplements: A Comprehensive Guide
- Achieve Your Leg Injury Recovery In Less Time
- Blood Sugar Control: Effective Ways to Manage Diabetes